How to Choose the Perfect Heat Sink for Your Computer Build!
Discover the essential guide to heat sinks for computers. Explore types, benefits, and installation tips to enhance your system's cooling efficiency.
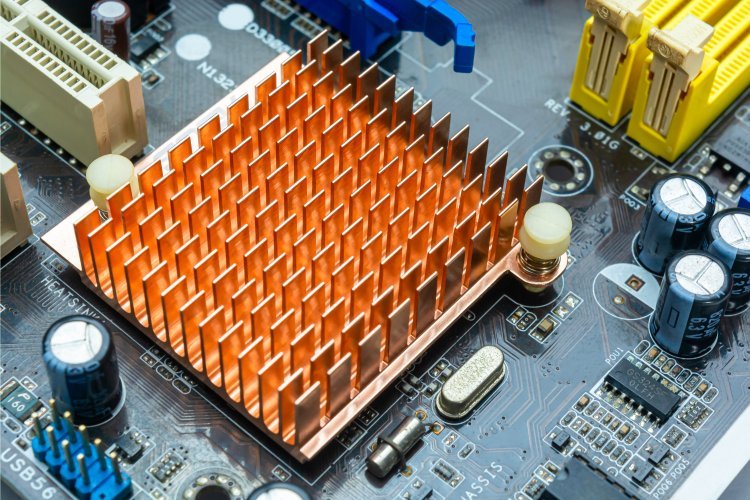
When building a computer, one of the most crucial components to consider is cooling. Proper cooling ensures that your system runs smoothly, efficiently, and with longevity. Among the various cooling solutions available, the heat sink is an essential part of your computer build, playing a significant role in preventing your hardware from overheating. Whether you're assembling a high-performance gaming rig, a workstation for video editing, or a powerful server, selecting the perfect heat sink for your computer can make all the difference.
The right heat sink will keep your components, such as the CPU, GPU, and storage devices, at an optimal temperature, allowing them to perform at their best without the risk of thermal throttling or damage.
Why Cooling is Important for Your Computer Build
The Role of Heat in Computer Performance
Heat is an inevitable byproduct of any electronic device that processes data, and computers are no exception. Modern CPUs, GPUs, and other critical components work at lightning-fast speeds to execute complex calculations and handle intense workloads. However, this level of performance generates substantial heat that can interfere with their functionality if not properly managed.
When a computer gets too hot, its components may slow down to prevent damage, a process known as thermal throttling. In extreme cases, sustained high temperatures can cause permanent damage to the hardware. To avoid these issues, effective cooling is a must, and that’s where heat sinks for computers come into play.
What Happens When Your Computer Overheats?
Overheating leads to several problems:
-
Reduced Performance: Heat causes components like the CPU and GPU to throttle their speed, resulting in slower processing times and lag during tasks like gaming or video rendering.
-
Reduced Lifespan: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause permanent damage to sensitive components, significantly shortening their lifespan.
- System Instability: Overheating can cause system crashes, freezes, or even data corruption.
To prevent these problems, a reliable cooling solution like a heat sink is essential to maintain your computer’s performance and stability.
How Does a Heat Sink Operate?
Heat Sink Basics
A heat sink is a device designed to absorb and dissipate heat from an electronic component, such as the CPU, GPU, or storage drives. Heat sinks are made from materials with high thermal conductivity, like aluminum or copper, which allow them to efficiently transfer heat away from the component.
The heat sink works by making direct contact with the heat source (e.g., the CPU), absorbing the heat, and then dispersing it into the surrounding air. Some heat sinks also incorporate fans to enhance the cooling process, while others rely solely on passive cooling through surface area and material properties.
How Heat Sinks Keep Your Components Cool
Heat sinks help maintain the temperature of your components at safe levels, preventing overheating. They are designed to maximize the surface area for heat dissipation, which is why you often see heat sinks with fins or other intricate designs. The larger the surface area, the more heat the heat sink can transfer to the surrounding air, keeping your system cool.
Types of Heat Sinks
Air Cooling vs. Liquid Cooling
When choosing a heat sink, you’ll generally encounter two main cooling methods: air cooling and liquid cooling.
-
Air Cooling: This is the most common form of cooling for most computer builds. Air coolers consist of a heat sink paired with a fan to help move air over the surface area, expelling heat efficiently. Air cooling is typically sufficient for most users, especially for moderate to high-performance PCs.
-
Liquid Cooling: In more advanced systems, liquid cooling uses a closed loop of liquid to transfer heat from the CPU or GPU to a radiator, where the heat is expelled. Liquid cooling is often used in high-end gaming rigs or workstations that require exceptional cooling performance, especially for overclocked systems.
Active vs. Passive Cooling Systems
-
Active Cooling: This involves using fans or pumps to actively push air or liquid across the heat sink, providing better cooling efficiency. Active cooling systems are more effective in scenarios where high heat generation occurs.
-
Passive Cooling: In passive cooling, the heat sink relies solely on natural convection, with no moving parts. It is generally quieter but less effective at cooling compared to active systems.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Heat Sink
- Size and Compatibility
Before purchasing a heat sink, it's crucial to ensure that it is compatible with your system. Consider the size of your CPU or GPU socket and make sure the heat sink you choose fits the mounting points. Overly large or small heat sinks may not provide the best cooling efficiency.
- Material Considerations
Heat sinks are made from various materials, each with its benefits. Copper, for example, offers superior thermal conductivity, making it an excellent choice for high-performance systems. However, it’s also heavier and more expensive. Aluminum, on the other hand, is lighter, cheaper, and still provides excellent cooling performance, making it a common material for mainstream builds.
- Airflow and Fan Configuration
Airflow plays a significant role in the effectiveness of your heat sink. When selecting a heat sink, take into account the fan configuration and how it will interact with the rest of your system. Proper airflow ensures that hot air is directed away from your components, reducing the chances of overheating.
- Noise Levels
Some heat sinks, especially those with fans, can generate noise. If you are sensitive to noise or if you are building a quiet PC, look for a heat sink designed with noise-reducing features, such as low-RPM fans or passive cooling options.
Choosing the Right Heat Sink for Different Computer Components
- CPU Heat Sinks
When selecting a heat sink for your CPU, make sure it has enough surface area and cooling capacity to handle the demands of your processor. High-performance CPUs, especially those used for gaming, content creation, or server applications, require robust cooling solutions to prevent throttling.
- GPU Heat Sinks
Similarly, GPUs also generate significant heat during intensive tasks like gaming and rendering. A powerful GPU heat sink paired with an effective fan or liquid cooling system is essential for preventing performance issues and maintaining system stability.
- SSD and Storage Heat Sinks
While SSDs don’t generate as much heat as CPUs or GPUs, high-end models, especially those with NVMe interfaces, can still benefit from additional cooling. Installing an SSD heat sink can help prevent overheating and improve performance, particularly when dealing with large files or extensive read/write operations.
How to Match Your Heat Sink to Your Computer Build
-Gaming PC Build
For gaming PCs, choose a heat sink that can handle the heat generated by powerful CPUs and GPUs. Air coolers with large heatsinks and high-performance fans are ideal, though liquid cooling systems are also an option for top-tier builds.
- Workstation Build
Workstations used for video editing, 3D rendering, or data processing require advanced cooling solutions to manage the heat generated by professional-grade components. High-performance air or liquid cooling systems are often the best choice for such builds.
- Server Build
Servers often run 24/7 and handle intensive workloads. A reliable and efficient cooling solution is necessary to keep the system running smoothly. Consider high-efficiency heat sinks with robust airflow and cooling capacity.
Heat Sink Installation Guide
Step-by-Step Instructions for Proper Installation
-
Prepare the Surface – Clean the CPU or GPU and the heat sink surface.
-
Apply Thermal Paste – Apply a small amount of thermal paste to ensure proper heat transfer between the CPU and the heat sink.
-
Install the Heat Sink – Align the heat sink with the mounting points and securely attach it.
-
Check for Proper Fit – Make sure the heat sink is firmly in place and has good contact with the component.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-tightening screws can damage the component or warp the heat sink.
- Insufficient thermal paste can result in poor heat transfer.
Maintaining and Cleaning Your Heat Sink
To keep your heat sink functioning optimally, regularly clean it to remove dust and debris. Over time, dust buildup can obstruct airflow, reducing cooling efficiency.
Choosing the right heat sink for your computer is crucial for ensuring its performance and longevity. By considering factors such as size, material, airflow, and compatibility, you can select the ideal cooling solution for your system. Whether you’re building a gaming rig, workstation, or server, a good heat sink will help keep your components cool, preventing overheating and improving your overall computing experience.
FAQs
How do I know if my computer needs a heat sink?
If your system is overheating, experiencing throttling, or running into stability issues, a heat sink is essential.
Can I use any heat sink for my CPU?
No, make sure the heat sink is compatible with your CPU’s socket type and size.
Do heat sinks make a noticeable difference in performance?
Yes, a good heat sink prevents thermal throttling, which can significantly improve your system's performance.
How often should I clean my heat sink?
It’s recommended to clean your heat sink every 3-6 months, depending on the dust levels in your environment.
Are liquid cooling systems better than air cooling for gaming PCs?
Liquid cooling systems are generally more effective at cooling, but they are also more expensive and complex to maintain.
What's Your Reaction?
















