Magnesium Selenate Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2025: Manufacturing Plant Setup and Operations
Introduction
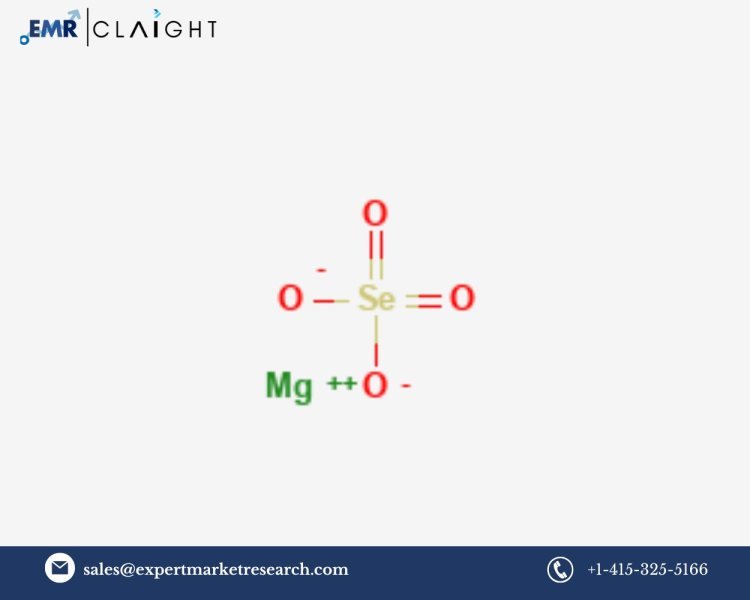
Magnesium selenate is a chemical compound that plays an essential role in various industrial applications, especially in the agricultural and pharmaceutical sectors. It is commonly used as a nutrient source in fertilizers, as selenium is an important micronutrient for plants, enhancing growth and resistance to diseases. Magnesium selenate also finds applications in the production of specialized chemicals, as a catalyst in certain reactions, and as a dietary supplement in trace amounts for animals and humans. The Magnesium Selenate Manufacturing Plant Project Report provides a comprehensive guide for entrepreneurs and investors looking to set up a manufacturing plant for magnesium selenate. This report covers key aspects such as market analysis, raw materials, production processes, required equipment, financial projections, and regulatory considerations for successfully establishing a manufacturing unit for magnesium selenate.
Market Overview and Growth Prospects
Magnesium selenate's unique properties make it highly valuable in several key industries. Some of its primary applications include:
-
Agriculture: Magnesium selenate is primarily used as a fertilizer or soil additive. Selenium is a critical micronutrient that plants require for proper growth. It plays a key role in photosynthesis, respiration, and nitrogen fixation, and it helps plants resist diseases, pests, and environmental stress.
-
Animal Feed Supplements: Selenium, an essential micronutrient for livestock, is often supplied in the form of magnesium selenate in animal feed. It helps enhance immunity, growth, reproduction, and overall health of farm animals.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Magnesium selenate is sometimes used in the formulation of pharmaceutical products, especially those related to animal nutrition. It is also used in some trace mineral supplements for humans and animals.
-
Cosmetics: Due to its antioxidant properties, magnesium selenate is occasionally incorporated into cosmetic formulations aimed at improving skin health.
-
Industrial Applications: Magnesium selenate also has potential applications as a catalyst in chemical reactions, as a reagent in research, and in other specialized industrial processes.
As industries like agriculture and pharmaceuticals continue to grow, the demand for magnesium selenate is expected to increase. The growing focus on sustainable farming practices, the need for trace elements in livestock feed, and the increasing awareness of the benefits of magnesium and selenium in human nutrition all point to a bright future for the magnesium selenate market.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Growth Drivers
Several factors are contributing to the growing demand for magnesium selenate:
-
Increasing Agricultural Demand: With the global population continuing to rise, the demand for food is also growing. This drives the need for fertilizers that enhance crop yield and improve the nutritional content of plants. Magnesium selenate’s role in promoting plant health and resistance to diseases makes it a valuable component in modern agricultural practices.
-
Focus on Sustainable Agriculture: There is an increasing shift toward sustainable and organic farming practices, which emphasizes the use of bioavailable nutrients for plants. Magnesium selenate fits this trend as it provides a natural and effective way to supplement selenium in soil.
-
Growth in Livestock Industry: As global meat and dairy consumption rises, the need for high-quality animal feed with essential micronutrients like selenium becomes more critical. Magnesium selenate is a safe and effective way to provide selenium in animal diets.
-
Health Consciousness and Wellness: There is a rising awareness of the importance of trace minerals such as selenium in human and animal health. Magnesium selenate is used in dietary supplements, contributing to its growing demand in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical sectors.
-
Government Regulations and Subsidies: In some countries, governments support the use of trace minerals in agriculture, livestock, and human health through subsidies, grants, or regulatory support. This further drives the demand for magnesium selenate.
Key Components of a Magnesium Selenate Manufacturing Plant
The establishment of a magnesium selenate manufacturing plant involves several important components. Below is a detailed explanation of each element of the process.
1. Raw Materials
The primary raw materials required to produce magnesium selenate include:
-
Magnesium Oxide (MgO): Magnesium oxide is a key component that combines with selenium compounds to form magnesium selenate.
-
Selenium (Se): Selenium is typically sourced as sodium selenate (Na₂SeO₄) or selenium dioxide (SeO₂), which reacts with magnesium oxide to produce magnesium selenate.
-
Water: Water is used to dissolve and combine the raw materials during the production process.
The quality and availability of these raw materials are vital to the production process, and reliable suppliers must be identified to ensure a consistent supply.
2. Manufacturing Process
The production of magnesium selenate follows a relatively straightforward chemical process that involves reacting magnesium oxide with selenium compounds. Below is a step-by-step outline of the process:
Step 1: Reaction of Magnesium Oxide and Selenium Compound
Magnesium oxide is mixed with a selenium compound, such as sodium selenate, in a reaction vessel.
Step 2: Purification
The resulting mixture may contain impurities such as unreacted materials and byproducts. To ensure the purity of magnesium selenate, the mixture is subjected to a purification process, often involving filtration, washing, and recrystallization.
Step 3: Precipitation
Magnesium selenate is precipitated from the solution by evaporating excess water. This crystallizes the compound into a solid form, which is then separated and collected.
Step 4: Drying
The precipitated magnesium selenate is dried to remove any remaining moisture. This is typically done using rotary dryers or other industrial drying methods to ensure that the product is in a stable, free-flowing powder form.
Step 5: Packaging
After drying, the magnesium selenate powder is packaged in appropriate containers for storage and shipment. The packaging must be airtight and moisture-resistant to maintain the product's quality.
3. Manufacturing Equipment
The production of magnesium selenate requires various pieces of specialized equipment to ensure the reaction and purification processes are carried out effectively. The essential equipment includes:
-
Reaction Vessels: These are used to mix and react magnesium oxide with selenium compounds. These vessels should be made from materials resistant to corrosion and chemical reactions.
-
Filtration Units: These are used to separate impurities and unreacted materials from the magnesium selenate solution.
-
Evaporators: These are used to remove excess water from the solution, promoting the precipitation of magnesium selenate.
-
Drying Equipment: After precipitation, the product is dried using drying equipment such as rotary dryers, fluidized bed dryers, or vacuum dryers to remove moisture.
-
Packaging Machines: Automated packaging machines are used to pack the final product into containers, ensuring it is sealed and protected from contaminants.
4. Plant Layout and Design
The layout of the magnesium selenate manufacturing plant is crucial for operational efficiency and safety. A typical plant layout includes:
-
Raw Material Storage: This area stores the raw materials, including magnesium oxide and selenium compounds, prior to use in the manufacturing process.
-
Reaction and Processing Area: This section houses the reaction vessels, filtration units, and evaporators necessary for producing magnesium selenate.
-
Drying and Packaging Area: After precipitation, the product is dried and packaged in this section to prepare it for shipment.
-
Quality Control Laboratory: A laboratory for testing the final product for purity, particle size, and moisture content. This area is vital for ensuring product quality.
-
Storage and Dispatch Area: Finished products are stored in this section before being dispatched to customers.
5. Quality Control and Regulatory Compliance
Maintaining high product quality is crucial in the manufacturing process. To achieve this, the plant must implement strict quality control measures, including:
-
Purity Testing: Regular testing to ensure that the magnesium selenate meets purity standards for agricultural, pharmaceutical, and industrial uses.
-
Particle Size Testing: The particle size distribution is essential for the effectiveness of magnesium selenate in agricultural and industrial applications. Consistent particle size is crucial for its application as a fertilizer or supplement.
-
Moisture Content Testing: Excess moisture can affect the stability and handling of the product, so moisture content must be closely monitored.
-
Regulatory Compliance: The plant must comply with local, national, and international regulations regarding chemical production, waste disposal, and environmental protection. The plant should also adhere to industry standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management.
6. Financial Projections and Investment Considerations
Setting up a magnesium selenate manufacturing plant requires significant capital investment. The following financial aspects should be considered:
-
Capital Investment: Initial investment includes land acquisition, plant construction, machinery purchase, and raw material procurement.
-
Operating Costs: Ongoing expenses include labor, utilities (such as energy for drying processes), raw materials, and maintenance.
-
Revenue Generation: Revenue will come from selling magnesium selenate to the agricultural, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries. Pricing should be competitive with industry standards.
-
Return on Investment (ROI): Detailed financial projections, including ROI, break-even analysis, and payback period, are necessary to evaluate the profitability of the plant.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au
What's Your Reaction?













